1. Safety, Health, and Environment System
1.1. Safety, Health, and Environment Policies
Under the framework of social responsibility and safety, health and environment (SHE) management system, FTC shall follow SHE policies, stipulate regulation identification, and periodically gathers relevant applicable regulations of identification, integration, audit, and conformity assessment for a good start on safety, health and environment management. For continuous emphases on such management and implementation of that system, we make a commitment to the following policies:
- Ensure compliance with relevant safety, health, and environment regulations and other reasonable demands of stakeholders.
- Make good use of the Safety, Health, and Environment Administration System to strengthen pollution prevention and reduce hazardous impacts.
- Promote hazard identification, risk evaluation, and risk control to prevent damage and health hazards.
- Promote energy conservation and reduction to reduce the impacts of environmental damage and hazards to health and safety.
- Strengthen neighboring relationships, establish good communication channels, enforce routine inspections, ensure reviews, and seek continuous improvements.
1.2. Occupational Health and Safety Management System
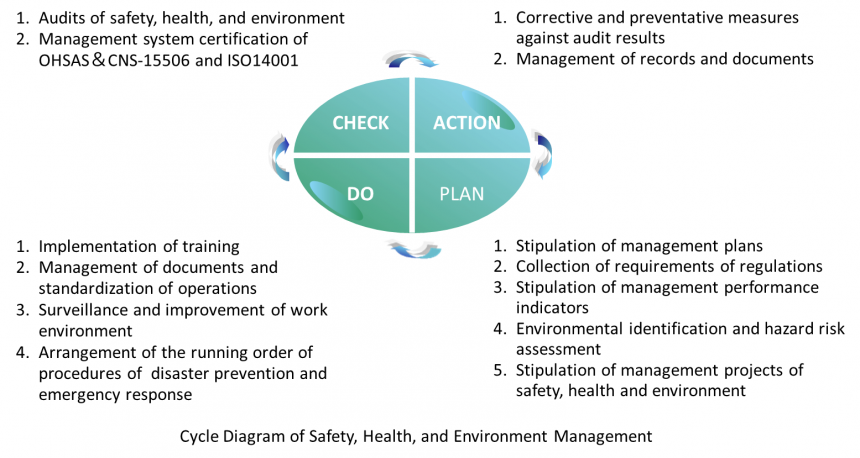
Founded in 1973, FTC has been in conformity with governments’ policies and actively made contributions to the economic development and social prosperity. Under the business philosophy that environment, safety, health and economy should be given equal emphases, FTC has taken hazard identification and risk management into consideration for health and safety management. To fulfill objectives of health and safety management, FTC adopts the PDCA cycle (Plan, Do, Check and Action), puts all operations, safety and health related affairs into standardization, documentation, and procedures, continuously conducts examinations and discovers problems for instant corrections, and implements continuous improvements and enhances the performance of health and safety management trough risk management. Certification of OHSAS-18001/CNS-15506 has been renewed once every three years since June 2009. In line with the international current of safety and hygiene, FTC dedicates to promoting the health and safety system management. In November, 2019, FTC started to launch ISO 45001 training courses and obtained ISO 45001:2018 Safety and Hygiene Management System in June, 2020.
1.3. Environmental Protection Management System
With the business philosophy—richly cultivating Taiwan, reaching out to the world and sustainably growing—and deep realization that the social environment, climate change and business management are inseparably connected, FTC has made its commitment to environmental management, such as pollution prevention and control, research and development of eco-friendly processes/products, efficiency enhancement to energy-saving and reduction of emissions/effluent/waste, and so forth.
1.4. Work Environment and Employees' Safety and Health
1.4.1. Chemicals Management
To prevent hazards of hazardous chemicals, a written Hazard Communication Program is formulated to ensure that all workers are knowledgeable about those potential hazards and that the usage conforms to the hazard communication standard. To further avert hazards as a result of the spill of chemicals, for sites that chemicals are stored and the periphery of equipment, such as storage tanks, pumps, etc., spill prevention dikes with adequate height or similar mechanisms with spill prevention function are installed. Moreover, FTC will routinely educate and train workers to correctly use personal protective equipment (PPE) contingent to the surroundings of the workplace and adopted chemicals and oversee how workers use that equipment at work. The promotion of the plan requires the supervision and promotion of relevant departments, plants, and plant directors, as well as the cooperation of relevant departments, plants, and Industrial Safety & Hygiene Officers in the implementation of the following items:
1. Compilation and organization of the Hazardous Chemical Inventory.
2. Preparation of the floor layout of the plant for the storage location of hazardous chemicals.
3.Preparation of the labeling for hazardous chemicals.
4.Examination of the “Safety Data Sheet” of the hazardous chemicals and review of the accuracy of the contents in the Safety Data Sheet and timely updates as required by the actual conditions.
5.Preparation of the relevant mark of the hazardous chemicals.
6.Supervision of personnel training for the “General Knowledge of the Manufacturing, Handling, and Usage of Hazardous Chemicals.
7.Assisting the Industrial Safety & Hygiene Office in the General Knowledge of Hazards promotion campaign.

Movable Spill-proof Pallet for Chemical Storage

Fixed Chemical Storage Tank for Spill Avoidance
1.4.2. Work Environment Management
To protect workers’ safety and health thorough understanding of the work environment, FTC establishes the Surveillance Assessment Group to draw up the Work Environment Surveillance Program that is based on sampling results of conditions of the work environment and worker exposures, and asks specialized third-party environmental testing organizations to conduct regular inspections of the work environment. In view of industrial characteristics, employee noise exposures in some of FTC’s sites are relatively high. To prevent hearing loss from workplace noise, FTC has traced workers’ health conditions through reviewing their previous special health examination records and conducting noise exposure sampling for those who work in sites with higher noise exposures, trained workers for hearing protection, taken noise measurements, purchased adequate and effective hearing protectors (earplugs or muffs), required workers to wear such equipment, and asked each unit to strengthen isolation of noise sources.
1.4.3. Health Management and Health Promotion
(1)General Health (Physique) Examination
Before new employees report for work, they must proceed to designated certified hospitals or medical institutions for general health examination and complete the “Employee Health Examination Booklet”. Employees and workers should comply with the following regulations to regularly undergo general health examinations. The inspection frequencies are once every 5 years for those who are under 40 years old, once every 3 years old for those who are between 40 and 65 years old, and once every year for those who are over 65 years old.
(2)Special Health (Physique) Inspection
For new employees working in especially hazardous operations, they should undergo a Special Health (Physique) Inspection at designated certified hospitals for inspection items stipulated by the regulations of the special hazard workplace within one week of reporting for work. The results of the inspection will be used for comparison with the “Diseases Deemed Unfit for Operation” as the basis for dispatching work. A worker who is assigned to the workplace with specific hazards or dispatched from one such workplace to another must take a special health examination on legally specified items operated in that newly assigned workplace before such assignment becomes effective. If the examination result reveals that the working circumstances are not friendly to that worker, no such assignment will be executed. For current employees working in especially hazardous workplaces, the Company will implement the Special Health (Physique) Inspection annually in accordance with regulations.
(3)Onsite Physician Services
In accordance with the onsite service frequency and staffing requirements of the “Staffing and Onsite Service Frequency of Physicians Conducting Labor Health Services” and “Staffing of Nurses Conducting Labor Health Services” stipulated in the “Labor Health Protection Regulations”, the Company has employed or commissioned physicians and nursing personnel to offer onsite labor health services.
(4)Emergency Medical Care
Due to the increasing threat of cardiovascular diseases to human health in recent years, the 1st and 2nd Plant in Taiwan have established Automated External Defibrillators (AED) in the Security Offices of both plants to strengthen emergency medical care. When the Security Office receives an emergency report, they will immediately notify medical and industrial safety personnel and then dispatch an ambulance to the location of the report for emergency patient transport. The ambulance will be equipped with an AED and other necessary medical equipment in order to be prepared for other unexpected situations. The Plant infirmary is responsible for the maintenance of the AED, as well as organizing regular AED operation training sessions.

Automated External Defibrillators (AED),
in place in FTC's 1st and 2nd Plants
 Company Ambulance
Company Ambulance
(5)Employee Welfare
- Establish of the mutual aid committee
- When employees and their families seek medical services at Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, they are entitled to discounts for the medical expenses unsubsidized by the health insurance policy, as well as discounts for health inspections.
- Outstanding employees are nominated each year and awarded with prizes and rewards.
- Employee travel allowance
- Staff fitness equipment, parking lot
- Opportunities of comprehensive training as well as continuing education for employees.
- Meal subsidy for employees on weekdays and gift money as a substitute for year-end dining party
- Birthday cash gifts, well-fare money for Dragon Boat Festival/Moon Festival, scholarship for employees and offspring; Labor Day gifts given via the trade union
- Establishment of recreational buildings, hostels, Single dormitories, and family dormitories for employees who are outlanders
- Discounts at contracted clinics and merchants and establishment of convenience stores in the Taiwan Plant in March 2019.
(6)Health Promotion Campaigns
With regard to conducting workplace health promotion campaigns, the Company will plan and organize activities, such as health education and health guidance, and other related health promotion activities every year.
 Free Services for Cancer Screening of 4 Main Cancers
Free Services for Cancer Screening of 4 Main Cancers
 Stress Relief Lecture for Employees
Stress Relief Lecture for Employees
 Training in CPR & AED
Training in CPR & AED
 FTC Cup Match in Badminton
FTC Cup Match in Badminton
 FTC Cup Match in Volleyball
FTC Cup Match in Volleyball
 Outdoor Activity Held by the Mountaineering Club
Outdoor Activity Held by the Mountaineering Club
1.5. Regulations for Safety, Health and Environment
FTC stipulates corresponding regulations\rules of safety, health and environment protection to require the internal and suppliers to cooperate in realization of corporate social responsibility. These regulations\rules are listed as follows:
| Mission Required for the Internal or Suppliers |
FTC's Baseline |
| Management of Legal Compliance |
Regulations for Identifying and Ensuring Compliance with Legal and Other Requirements |
| Air Pollution Control |
Air Pollution Control Regulations |
| Water Pollution Control |
Regulations for Wastewater Management |
| Waste Management |
Regulations for Waste Management |
| Toxic Chemical Substances Control |
Regulations for Toxic Chemical Substances Control |
| Management of (Raw) Materials |
Rules Governing Materials |
| Chemicals Labeling and Control |
Regulations for Chemicals Labeling and Control |
| Material Supplier Evaluation |
Regulations for Material Supplier Evaluation |
| Engineering Management |
Engineering Management Rules |
| Hire of Safety, Health and Environment Management |
Regulations Governing Undertakers of Safety, Health and Environment Management |
| Engineering Contractor Evaluation |
Regulations of Engineering Contractor Evaluation |
| Hazards Analyses of Construction |
Regulations Governing Analyses of Work Safety |
| Management of Environmental Cleanliness Maintenance |
Regulations Governing Environmental Cleanliness Maintenance of the Public Area |
| Food Sanitation |
Regulations of Ingredient Supplier Evaluation |
| Tobacco Hazards Prevention |
Regulations Governing Non-smoking for Protecting Workplace Safety and Employee Health |
| Environment Monitoring |
Regulations Governing Work Environment Monitoring |
2. Environmental Protection Improvements
2.1. Air Pollution Control
FTC has worked on all kinds of air pollution control and install appropriate equipment, such as Wet Flue Gas Desulfurization, EP Electrostatic Oil Mist Collector, Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) Denitrification, Pre-sprinkling Scrubbing Tower, Activated Carbon Tower, PVOCs reclamation devices, applying Fluidized-Activated-Carbon (with built-in Adsorption /Desorption Towers), etc., for emissions of flues that are generated from various processes. Furthermore, heat recovery system and Oxygen combustion control system are installed one by one for boilers to conserve the consumption of fuel and reduce emissions. SOP of pre-maintenance, repairs, training and operation are also stipulated for the optimization of all control equipment and the effectiveness of emission control. The summarized information of expenditures over years of installed emission control equipment is as follows:
| Air Pollution Control Equipment List |
| 1st Plant |
2nd Plant |
| Plant |
Amount (NT$) |
Plant |
Amount (NT$) |
| 1st Area of Engineering Plant |
513,420,000 |
2nd Area of Engineering Plant |
7,680,000 |
| 1st Area of 1st Dyeing Plant |
68,738,734 |
1st Area of 2nd Tire Cord Plant |
110,633,924 |
| 1st Area of 2nd Dyeing Plant |
26,588,400 |
2nd Area of 2nd Tire Cord Plant |
53,761,275 |
| Printing Plant |
6,072,400 |
Subtotal |
172,075,199 |
| 1st Tire Cord Plant |
51,786,606 |
|
|
| 1st Area of Processing Plant |
93,267,000 |
|
|
| 2nd Area of Processing Plant |
90,834,550 |
|
|
| Plastic Plant |
990,000 |
|
|
| Subtotal |
851,697,690 |
|
|
| Accumulated amount of investment in air pollution control equipment (as of the end of 2022): NT$1,023,772,889 |
FTC acquires legal air pollution operating permits for all processes, having each emission flue regularly inspected and inspection results reported to the Environmental Protection Bureau (EPB). Pulse Jet Baghouses, Electrostatic Precipitators, Flue Gas Desulfurization, etc. are in place for cogeneration, and the Continuous Emission Monitoring System (CEMS) is further installed and connected to the EPB’s system to allow EPB to supervise FTC’s operation.
All heat setting machines of D&F plants and all dipping machines of tire cord plants are equipped with scrubbers and electrostatic oil mist collectors to collect waste gas and eliminate part smoke and oil mist and unpleasant smell. For VOCs reduction, Condenser plus VOCs reclamation devices, applying Fluidized-Activated-Carbon (with built-in Adsorption /Desorption Towers) are installed and multiple control equipment is adopted to collect fugitive emissions and emissions of flues to attain targets of VOCs reduction by removing more than 90% of VOCs of processes. All results of qualified testing organizations’ measurements meet not only emission standards but also legal requirements of the Environmental authorities’ on-site audits.
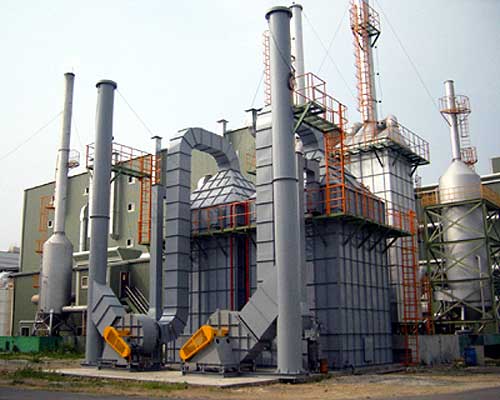

Electrostatic Oil Mist Collector

VOCs reclamation devices, applying Fluidized-Activated-Carbon (with built-in Adsorption /Desorption Towers)
2.2. Noise
To effectively keep noise nuisance from worsening living quality of the neighborhood community, besides engineering advances, FTC establishes noise barriers around the periphery of the factory sites and asks qualified testing institutions, approved by the Environmental Analysis Laboratory of the Environmental Protection Administration of the Executive Yuan, for noise measurement. All those measurement results meet requirements.
2.3. Effluents
Pursuant to the environmental regulations, FTC stipulates the water pollution prevention regulations in conformity with the Acts. In addition, FTC promotes projects to eliminate the wastewater and strictly manages the effluents to ensure that the quality of wastewater comply with the effluent standard and reduce the impacts on the environment.
In January, 2021, red-color dye was used in multiple manufacturing process at the same time, causing the effluents appearing to be red with relevant reports that the wastewater turned the creek into red. Although the continuous monitoring systems connected to environmental protection bureau (EPB) or EPB’s inspections showed that all figures of FTC wastewater including coloring figures complied with the effluents standard by the government, FTC felt sorry for the incident that causing the pubic panic and a bad impression. Therefore, FTC’s senior-level formed a relevant unit to implement the following measures to prevent the incident from happening again:
- Dedicated purposes for dedicated equipment:
12 equipment in D&F plants are designated for red-color dying, and the wastewater with highly red color are firstly stored to a storage container for the first procedure of discoloration before proceeded by the effluents systems to enhance the efficacy of discoloration.
- Process of discoloration and Visual Testing:
Red wastewater is stored to a container and discolored through chemicals. Operators will visually check the condition to decide for another discoloration or next process.
- Designated staff for inspection:
Adjusting the water level of the wastewater equalization basin#2 from 80% to 50% allows wastewater in abnormal conditions to be temporarily stored more than a day in case of any emergency. In addition, staff from D&F plants will be dispatched every four hour to check the color of the temporary wastewater basin and its condition to ensure compliance with the effluent standards.
- Establishment of Online Monitoring System:
Establishing continuous online monitoring system for coloring installed in the effluents basin and setting the internal control figure to 80 (the standard is 400) allow relevant operators and supervisors to manage the conditions in time. If any emergency happens, a text message will be sent to relevant personnel to take immediate action.
Upholding the spirits of ESG and sustainable development, FTC continues to renew the equipment, enhance the management and training of personnel, and implement various measures to protect the environment and create a win-win situation.
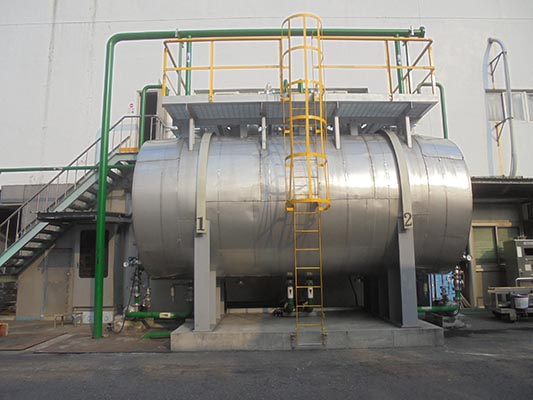  |
  |
| Pre-Processing Container for High Concentration of Red Dyeing (30 tons) |
Visual Testing for the Discoloration Result |
  |
  |
| Online Monitoring System for Coloring |
Interface of Online Monitoring System for Coloring |
2.4. Waste
In accordance with Waste Disposal Act, preparation of waste disposal plan shall be reviewed and approved by EPB before FTC conducts the disposal and clearance of waste in Taiwan Plant. The main waste is divided to Category D (General waste) and Category R (Recycling or reusing waste). The related information is registered and declared to EPB’s website, and each department conducts the internal management according to Regulations Governing Determination of Reasonable Due Care Obligations of Enterprises Commissioning Waste Clearance, including:
(1) Quarterly routine check and audit.
(2) Making out the check and audit record in writing which shall be properly retained for five years.
(3) Tracking the defect improvement status, and including it in the main points of the self-check and audit.
3.Energy Management Policy & Information of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
3.1 Impacts of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
(1) Risks of Relevant Regulations of Climate Change
A. It is expected that the Greenhouse Gas Reduction and Management Act by EPB will be renamed to Climate Change Response Act and amended within two years, and the Act is applicable to FTC.
B. According to the direction of amendments proposed by EPB in 2020, the significant change will be added the carbon pricing system, that is carbon fee. The carbon fee is expected to set NT$100/ton, and those fee will be collected for designated purpose such as the subsidy for emissions reduction plan. FTC’s safety and hygiene department will catch up with the amendments.
(2)Substantial Risks Brought by Climate Change
Extreme weather and climate change cause huge impacts on air pollution, ice melting, food, energy, flooding, wildfire, and raw material price and supply chains and so on. The climate change also influences the product sales; therefore, FTC take the measures as follows:
A. The extreme weather brings up the increase in the demand for the performance fabrics; for example, when blizzard occurs, the demand for cold-resistant fabrics will increase such as cold-resistant down jackets, thermal insulation fabrics, temperature-controlled smart clothing fabrics, and high-end waterproof and breathable fabrics and so on.
B. The global warming is unfavorable to down fabrics, but beneficial to the cooling fabrics. The risk should be shifted to the promotion of summer/autumn fabrics.
(3) Opportunites from Climate Change
A. FTC is aware that environmental issues (including climate issues) certainly impact on products.
*Branded customers put more and more emphasis on whether the material is environment-friendly, recyclable, or low-carbon emissions or not.
*Climate change changes the temperature patterns and makes the cycles of extreme cold and extreme heat unstable. Therefore, consumers’ demand on performance and multifunctional fabrics are increasing.
FTC is aware of the business opportunities of environmental and functional products, which has been integrated into our focus of long-term product development. It is estimated that it can bring up sales income.
B. R&D Strategy
Bio-based polyamide is applicable to sports and outdoor products. In 2021, we involve the resource to ensure the quality. Take PA410 (Bio-polyamide) as an example, a chemical extracted from biomass could be used as material. 70% of this bio-based chemical is made from extracts of caster oil. Planting of castor does not compete with people for food and caster can grow on barren land without a lot of irrigation. By using the bio-based renewable resources to replace non-renewable petrochemical resources can greatly reduce product carbon footprint. The product carbon footprint of petrochemical based PA66 is 6.5 kgCO2e whereas the product carbon footprint for PA4,10 is only 1.9 kgCO2e, which could reduce 70% of emissions.
(4) Whether (Direct, Indirect) GHG Emissions is validated by the Third Party or not
Since 2012, FTC has established the GHG emissions inventory organization to manage the document of GHG emissions and launch the related inventory procedure (including scope 1 and scope 2). In March, 2022, FTC commissioned SGS to conduct the Company’s 2021 GHG emissions and obtained the validation report and statement in compliance with EPB’s regulations. The relevant information was reported and disclosed on EPB’s GHG emissions platform.
FTC’s GHG emissions of 2021 amounted to 348,153 ton CO2e, including 254,887 ton CO2e of Scope 1 and 93,266 ton CO2e of Scope 2. For further information.
3.2 Strategies, Methods and Objectives of Greenhouse Gas Management
(1) Strategies for responding to climate change and greenhouse gases management
Climate change arising from global warming has threatened the survival of both animal species and mankind. In order to effectively control CO2 emissions and alleviate the impacts of global warming. FTC's Taiwan Plant decided to implement the ISO 150001 Energy Management System in 2015 to reduce both direct and indirect energy consumption and waste, precisely grasp energy conversion demands, improve the energy utilization efficiency and enhance the re-utilization rate of energy. The specific measures as follows:
A. Oil Conservation
- Installing waste heat recovery devices and oxygen control equipment onto exhaust chimneys of boilers and of production machinery.
- Installing condensed steam/hot water recycling devices for production equipment
- Replacing fuel with natural gas as the source of thermal energy for boilers and setting machinery
B. Air Conservation
- Designing well air circulation pipelines, installing gauges to measure on-site leakages, and regularly inspecting the air pipelines to avoid leakages.
- Managing compressors loads, splitting high and low pressures for use, and inhibiting the “false needs” of air compression for better operation efficiency of compressors and energy conversion efficiency.
C. Gas Conservation
- Recycling waste heat and condensed steam, using steam power cogenerations, and improving combustion efficiency of generation boilers.
- Improving efficiency of boilers for consumption reduction of all kinds of fuel.
D. Electricity Conservation
- Applying special materials and designs to the wind turbines of air conditioners and fan blades of cooling towers for less power consumption.
- Reducing electricity consumption by shortening the second-round circulation routes of all kinds of cooling water.
- Installing power saving devices in various motors.
- Using energy-saving lighting.
- Using high efficiency and energy-saving air compressors and chiller, cooling tower, etc.
(2) Objectives of GHG emissions Reduction
A. Taiwan Plant
FTC has stipulated the absolute targets of emissions reduction:
Short-term: Reduce 30% by 2025 from a base year, 2019.
Mid-term: Reduce 50% by 2030 from a base year, 2019.
Long-term: Reach to Carbon Neutrality in 2050.
B. Formosa Taffeta Co., Ltd. and subsidiaries (Group)
Formosa Taffeta Co., Ltd. has officially approved by the SBTi (Science Based Targets initiative, SBTi), becoming the first Textile company in Taiwan to be validated. With the worsening global climate change, FTC has been actively taking various energy saving and emission reduction measures to reduce the environmental impacts. In response to limit global warming to no more than 2°C, FTC committed to SBTi in July, 2022 and was officially approved on March 16, 2023. Formosa Taffeta Co., Ltd. commits to reduce scope 1+2 GHG emissions 26.3% by 2027 from a base year 2019, and also commits to reduce scope 3 GHG emissions 20% within the same timeframe.






 Company Ambulance
Company Ambulance
 Stress Relief Lecture for Employees
Stress Relief Lecture for Employees Training in CPR & AED
Training in CPR & AED FTC Cup Match in Badminton
FTC Cup Match in Badminton FTC Cup Match in Volleyball
FTC Cup Match in Volleyball Outdoor Activity Held by the Mountaineering Club
Outdoor Activity Held by the Mountaineering Club








